What Is Are Garment Spec Sheets and What Are They Used For?
A garment specification sheet, or just a spec sheet, is a vital tool used during the development process of a garment product. Spec sheets are mostly used in the fashion industry to communicate development ideas to a manufacturer. It contains key details of a product design, including technical sketches, color overview, etc.
In this post, we will look closer at what spec sheets are, what they contain, and the benefits of using them.
What is a Spec Sheet?
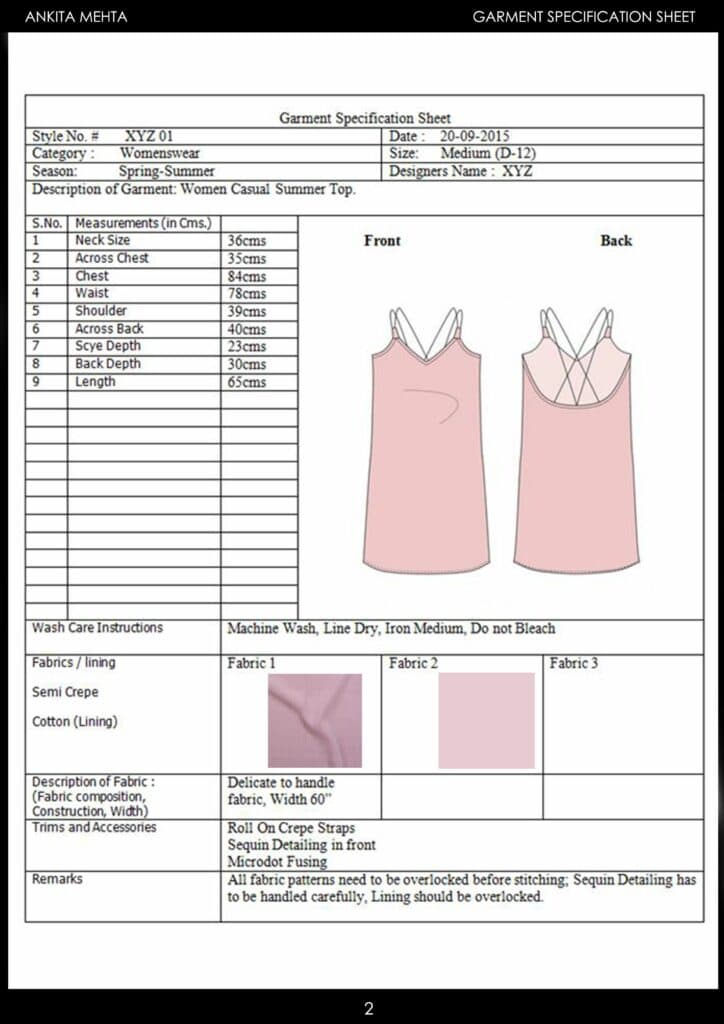
A garment spec sheet, or specification sheet, is a detailed document that provides all the necessary information about a garment design. It serves as a blueprint for manufacturers, ensuring that the final product meets the designer’s vision and quality standards.
You might be wondering if a spec sheet isn’t the same thing as a tech pack. Well, it’s not.
Spec sheets contain only key construction details needed to produce a finished garment. The detailed measurements and specifications included in the sheet are often referred to as garment specs. The key component of a spec sheet is a measurement chart (or measurement sheet). This chart contains all the measurements and locations for a clothing design.
Tech packs, conversely, contain both a spec sheet as well as other key details, including grading specification, BOM (Bill of Materials), etc.
Components of Garment Spec Sheets
A. Basic Information: The spec sheet starts with essential details such as the style number, season, date, and designer’s name. This helps in organizing and referencing the design efficiently.
B. Technical Sketches: Clear technical sketches of the garment from various angles (front, back, and side) are included to provide a comprehensive visual guide.
C. Measurement Details: Points of Measure (POM) specify where measurements should be taken. The size range and grading details ensure that the garment fits well across different sizes. Without accurate garment measurements, costly manufacturing errors might arise.
D. Fabric and Trim Information: Details about the fabric type, composition, and any trims used are specified to ensure the correct materials are used in production.
E. Construction Details: This section outlines the sewing techniques, stitch types, seams, and finishes required to construct the garment.
F. Colorways: Information about available color options, including Pantone numbers, is provided to maintain color accuracy.
Depending on the product, it might also contain the garment washing instructions.
Design faster and collaborate easier with manufacturers using Uphance PLM
What Are Spec Sheets Used For?
Spec sheets can be used for a variety of purposes, including:
1. As a Communication Tool: Garment spec sheets serve as a vital communication tool between designers and manufacturers, ensuring that production aligns with the designer’s vision.
2. Quality Control: They help maintain consistency and minimize errors, ensuring that each garment meets the required quality standards. Sharing samples with manufacturers, alongside the spec sheet, helps ensure the final product matches the designer’s intent and quality standards.
3. Costing and Pricing: Accurate cost estimation and budget management are facilitated by detailed spec sheets.
4. Production Planning: Spec sheets streamline the production process and aid in efficient resource allocation. The approved spec sheet serves as a key reference during bulk production to maintain consistency and manage quality.
The Benefits of a Garment Spec Sheet

1. Improved Accuracy
A garment spec sheet provides precise specifications for every aspect of a garment, from measurements to fabric types. Accurate patterns are created from the detailed specifications provided in the garment spec sheet. This level of detail ensures that manufacturers have clear guidelines to follow, significantly reducing the risk of errors and misunderstandings. With accurate instructions, the final product closely aligns with the designer’s vision, maintaining the integrity of the design.
2. Enhanced Collaboration
The garment spec sheet acts as a vital communication tool between designers and manufacturers. By clearly outlining every detail of the garment, it fosters better collaboration and understanding between all parties involved. This reduces the likelihood of miscommunications and helps to build a more cohesive and efficient workflow. Including a section for additional comments in the spec sheet allows designers to provide extra information or clarifications for manufacturers.
3. Time and Cost Efficiency
One of the most significant benefits of a garment spec sheet is its contribution to time and cost efficiency. Detailed specifications lead to fewer revisions during the production process, saving valuable time. Additionally, by minimizing errors and ensuring that the right materials and techniques are used from the start, overall production costs are reduced. This efficiency translates into faster turnaround times and more streamlined operations.
4. Quality Assurance
Maintaining high standards of quality is crucial in the apparel industry. A garment spec sheet helps ensure consistency in production, regardless of where or by whom the garment is manufactured. By adhering to the detailed specifications, manufacturers can produce garments that meet the required quality standards, which may vary depending on the brand and its specific requirements, leading to higher customer satisfaction and reduced returns.
5. Effective Production Planning
Garment spec sheets play a crucial role in production planning. They provide a comprehensive overview of all the materials, measurements, and construction techniques required for a garment. This helps in efficient resource allocation and planning, ensuring that all necessary components are available when needed and that the production process runs smoothly.
6. Accurate Costing and Pricing
With all the necessary details about materials, measurements, and construction techniques, garment spec sheets allow for precise cost estimation. This helps designers and brands set accurate pricing for their products, ensuring that they remain competitive in the market while also covering production costs.
Difference Between Spec Sheets and Tech Packs
It’s easy to confuse a spec sheet for a technical package, commonly known as a tech pack, largely because they are used for a similar purpose. However, there are salient differences between them.
The key difference is in the degree of extensiveness. Tech packs contain virtually every detail needed to bring a garment design idea to life. They include graded specs, spec sheets, Bill of Material (BOM), notes, care instructions, product images, etc. At the end of the day, you might have a tech pack with several pages.
Specification sheet, on the other hand, merges all the key details in a tech pack into a single sheet – or two depending on the use case. Think of it as a condensed form of a tech pack.
Another major difference is the use case. While a tech pack software is used for both development and marketing purposes, spec sheets are mostly used for the former.
Points of Measure and Garment Measurements
Points of measure (POM) are fundamental elements in any garment spec sheet, serving as the precise locations on a garment where measurements are taken to ensure the intended fit and design are achieved.
These points are carefully selected to capture the most critical dimensions of a garment, such as the high point shoulder, neck drop, sleeve opening, bottom hem, and neck seam. By clearly defining these points of measure, fashion brands and designers can communicate their expectations to manufacturers, ensuring that the finished garment aligns with the original vision.
Garment measurements are typically recorded from a sample size and then graded to accommodate a full size range, allowing for consistent fit across different sizes. The measurement chart, or measurement sheet, included in the garment spec sheet provides a detailed and visual representation of all the necessary dimensions. This chart is a vital tool in the tech pack, helping to maintain consistency and accuracy throughout the production process.


